| SPMODEL: A Series of Hierarchical Spectral Models for GFD | << Prev | Index| Next >> |
The governing equations and boundary conditions of a β-plane barotropic model on a two-dimensional double cyclic domain are as follows:
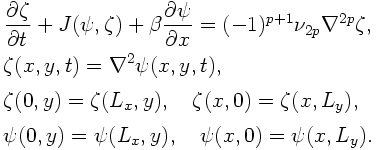
When the domain is infinite, there exists a solitary vortex solution called the "modon" ([8], [9]). The solution is expressed as follows with plane-polar coordinates (r,θ) whose origin is at the center of the vortex:
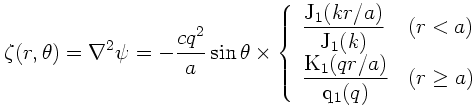
where a and c are the radius and the propagation speed of the solitary vortex, respectively. Here, q= √(β/c), and k is determined by
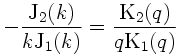
which is equivalent to the dispersion relation.
The resulting program source code is given as plbaro-beta_abcn_test3.f90. The Adams-Bashforth scheme is utilized for the time integration of the governing equation, although the Crank-Nicolson scheme is adopted for the dissipation term. The main part of the time integration is as follows:
do it=1,nt
ee_DVorDt = - ee_Jacobian_ee_ee(ee_StrFunc,ee_Vor) &
- Beta * ee_Dx_ee(ee_StrFunc)
ee_Vor = ( (1.0D0 - ee_HVisc*delta_t/2)*ee_Vor &
+ 3.0D0 * delta_t/2.0D0 * ee_DVorDt &
- 1.0D0 * delta_t/2.0D0 * ee_DVorDtB ) &
/(1.0D0 + ee_HVisc*delta_t/2)
ee_DVorDtB = ee_DVorDt
ee_StrFunc = ee_LaplaInv_ee(ee_Vor)
...
enddo
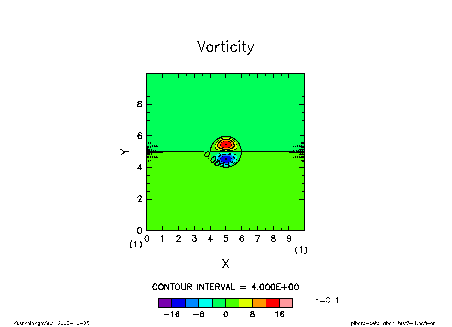
The picture below shows the time development of an initially given modon solution with a=c=1. You can observe how a solitary vortex propagates without changing its shape.
| SPMODEL: A Series of Hierarchical Spectral Models for GFD | << Prev | Index| Next >> |