| Development of a Cloud Convection Model for Jupiter's Atmosphere | << Prev | Index| Next >> |
The expression of saturation vapor pressure pvsw is adopted from eq. (14) of Briggs and Sacket (1989) [17].
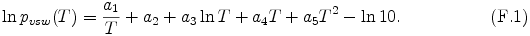
The coefficients a1 - a5 in eq. (F.1) are given by Table F.1. Note that the term -ln10 is added from the expressoin of Briggs and Sacket (1989) [17], since SI units are used instead of cgs units.
The latent heat per mole Lv is represented by using Clausius-Clapeyron equation and eq. (F.1) as follows.
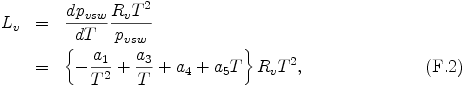
where Rv is the gas constant of each condensible species.
| Species | a1 | a |
a3 | a4 | a5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3(s) | -4122 | 41.67871 | -1.81630 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O(s) | -5631.1206 | -8.363602 | 8.2312 | -3.861449 × 10-2 | 2.77494 × 10-5 |
The equilibrium constant Kp in the NH4SH production reaction, H2S(g) + NH3(g) ↔ NH4SH(s), is adopted from eq. (19) of Briggs and Sacket (1989) [17].
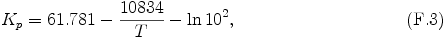
The term -ln102 has been added since SI units are used instead of cgs units.
The reaction heat per unit mol LNH4SH is represented by using the van't Hoff equation and eq. (F.3) as follows.
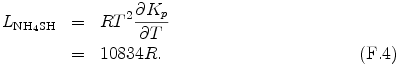
where R is universal gas constant.
| Development of a Numerical Model for Jupiter's Atmosphere | << Prev | Index| Next >> |