C. Details of the Model |
a. Basic Equations
For the basic equations, a 3D spherical primitive system is used (refer to Numaguti and Hayashi, 1991, and Numaguti, 1992, for details). For the horizontal and vertical directions, a latitude and longitude coordinate (λ, φ) system and a σ-coordinate system are adopted, respectively. The equations of motion, the continuity equation, the hydrostatic equation, the equation of water vapor, the thermodynamic equation, and the surface energy balance equation are as follows:
where
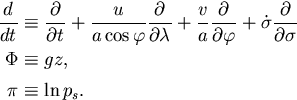
u, v are horizontal wind velocities,
is vertical wind velocity in σ-coordinates, T is temperature, q is specific humidity, ps is surface air pressure, Tg is surface temperature,
is geopotential, f is the Coriolis parameter, a is the radius of a planet, g is the gravitational acceleration, R is the gas constant of the atmosphere, cp is specific heat at constant pressure, and L s the latent heat of water vapor.
,
,
, and
are horizontal diffusion terms and Fuvdf, Fvvdf, FTvdf, Fqvdf are vertical diffusion flux terms. Sqcond is the specific humidity source term associated with condensation, Cg is the specific heat of the surface, which is set to 0 in practice. qrad, qvdfT, and qvdfq are net radiative flux, sensible heat flux, and latent heat flux terms, respectively.
Table 1 shows the values that are used for the parameters in the model. The value of the water vapor absorption coefficient,
, was determined using that at 1000 cm-1 in Figure 2 of Yamamoto (1952). The values of L and p0* are set identical to those in Nakajima et al. (1992).
Physical constants Universal gas constant R* = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 Gravitational acceleration g = 9.8 m s-2 Stefan-Boltzman constant σ = 5.67 × 108 W m-2 K-4
Table 1:Values of various constants and parameters used in model calculations.
Model parameters Molecular weight of dry air mn = 18 × 10-3 kg mol-1 Molecular weight of water vapor mv = 18 × 10-3 kg mol-1 Gas constant of dry air Rn = 461.9 J kg-1 K-1 Gas constant of water vapor Rv = 461.9 J kg-1 K-1 Specific heat of dry air at constant pressure cpn = 4Rn = 1616.6 J kg-1 K-1 Specific heat of water vapor at constant pressure cpv = 4Rv = 1616.6 J kg-1 K-1 Latent heat of water vapor L = 2.4253 × 106 J kg-1 Constant used in the saturated water vapor pressure equation p0* = 1.4 × 1011 Pa Mass of the non-condensable constituents in the atmosphere pn0 = 105 Pa Water vapor absorption coefficient κv = 0.01 m2 Kg-1 Dry air absorption coefficient κn = 0.0 m2 Kg-1 Radius of planet a = 6.37 × 106 m
It is assumed that saturated water vapor pressure can be given by
as in Nakajima et al. (1992).