|
3. Results: Dust-Free Case a. Diurnal Changes of Horizontal Mean Fields |
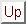


|
|
3.a.iv. Heat budget of the atmosphere and surface
|
Figure 3e shows diurnal changes of horizontal
mean heat budgets of the ground and atmosphere. In each panel, the
amount of net heating is nearly equivalent to that of cooling.
- Dominant components of the ground surface heat budget are
solar radiative heating and outgoing infrared radiative
cooling. Compared to these, the amount of sensible heat is quite
small.
- Dominant components of the atmospheric heat budget are infrared
radiative heating and sensible heating. Their total amount
reaches approximately 30 W m-2 during daytime.
|
Figure 3e: Diurnal changes of horizontal mean heat budgets for
the dust-free case on day 6. Units for the vertical axes is W m-2.
(Left panel) Heat budget for the ground layer. Blue line shows net
solar radiative flux
(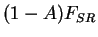 ),
red line shows net infrared radiative flux
( ),
red line shows net infrared radiative flux
(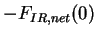 ),
green line shows sensible heat flux
( ),
green line shows sensible heat flux
(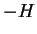 ),
and the orange line shows the total flux.
Positive sign indicates heating of the ground surface.
(Right panel) Heat budget of the atmosphere. Blue line shows net solar
(near infrared) radiative heating
( ),
and the orange line shows the total flux.
Positive sign indicates heating of the ground surface.
(Right panel) Heat budget of the atmosphere. Blue line shows net solar
(near infrared) radiative heating
(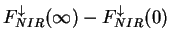 ),
red line shows net infrared radiative heating
( ),
red line shows net infrared radiative heating
(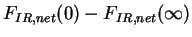 ),
green line shows sensible heating
( ),
green line shows sensible heating
(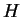 ),
purple line shows heating due to turbulent dissipation,
and the orange line shows the sum of net infrared radiative heating and sensible heating.
Positive sign indicates heating of the atmosphere. ),
purple line shows heating due to turbulent dissipation,
and the orange line shows the sum of net infrared radiative heating and sensible heating.
Positive sign indicates heating of the atmosphere.
|
|
A numerical simulation of thermal convection
in the Martian lower atmosphere with a two-dimensional anelastic model
Odaka, Nakajima, Ishiwatari, Hayashi,
Nagare Multimedia 2001
|


|
|