|
3.a.iii. Atmospheric heating profile
|
|
|
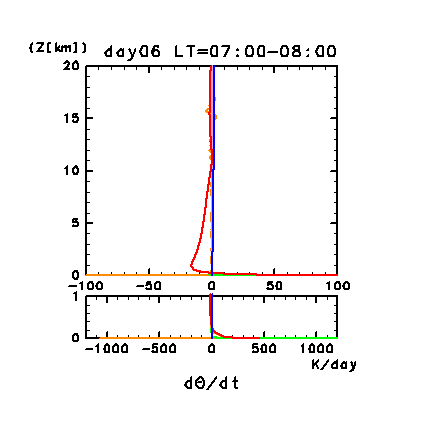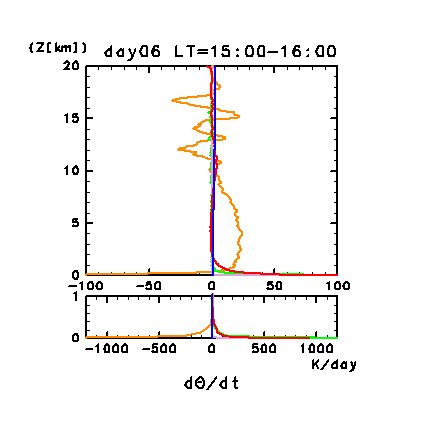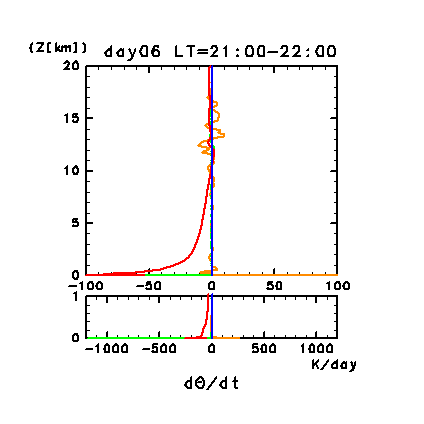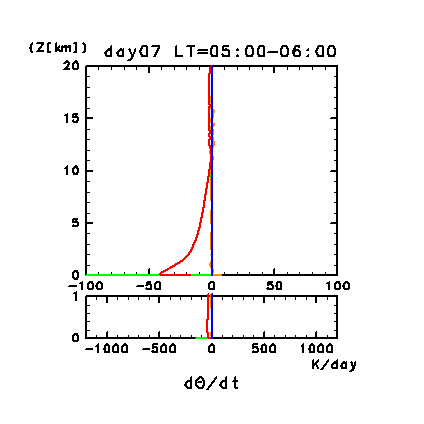
Figure 3d: Diurnal change of horizontal and time mean vertical
profiles of atmospheric heating rate (K/day) for potential temperature
for the dust-free case on day 6. Orange line denotes convective
heating, red line denotes infrared radiative heating, blue line
denotes solar radiative heating, green line denotes turbulent
diffusion of potential temperature, and light purple line denotes
heating due to turbulent dissipation. Lower panel shows a magnified
view of the profiles below 1 km.
|
Figure 3d shows the horizontal and time mean
vertical profiles of the atmospheric heating rate for potential
temperature. Below 2 km, daytime radiative heating increases
exponentially as height decreases. This is caused by
CO2 absorption of infrared radiation emitted
mainly from the ground. Radiative heating that is vertically uniform
above 4 km is caused by CO2 absorption
of near infrared radiation.
In a layer near the surface, there is heating due to diffusion of
sensible heat supplied from the ground and heating due to kinetic
energy dissipation. The magnitude of diffusive heating at the lowest
level is comparable with that of radiative heating. Heating due to
convection is negative near the surface, positive in the convective
layer and negative in the upper stable layer where convective plumes
penetrate. The magnitude of convective heating reaches to
approximately 100 K/day in the morning when the convective layer
thickness is small, and from 20 to 40 K/day in the afternoon when the
layer thickness is large. The depth of the convective cooling layer
near the surface is about 400 m, where the thermal boundary layer is
included.
The vertical profile of infrared radiative cooling during nighttime is
similar to that during daytime, but opposite in sign. The magnitude of
infrared radiative cooling gradually becomes small as the inversion
layer develops below an altitude of 2 km.
|