|
4.a.iii. Atmospheric heating profile (for days 1 and 2 of the dusty case)
|
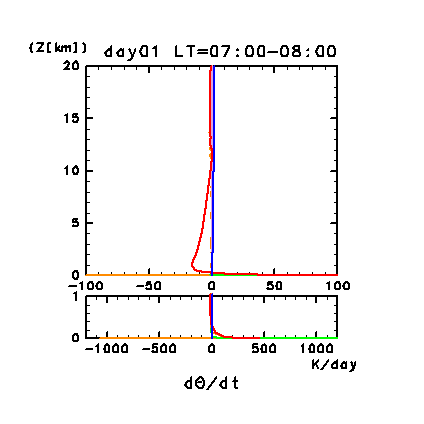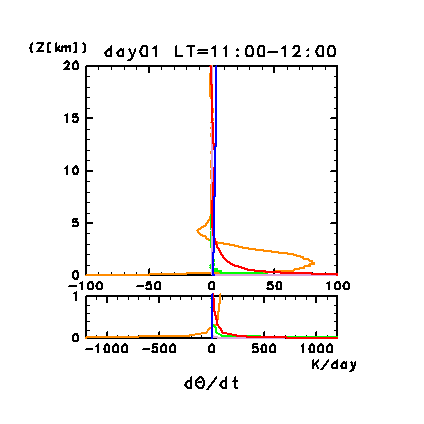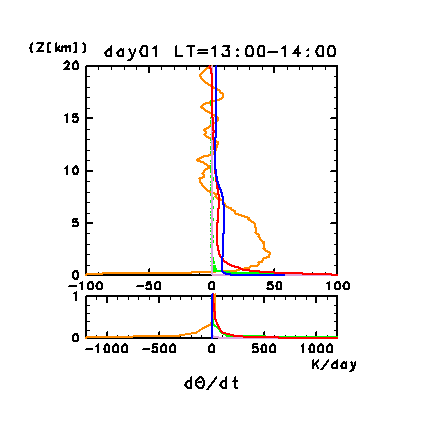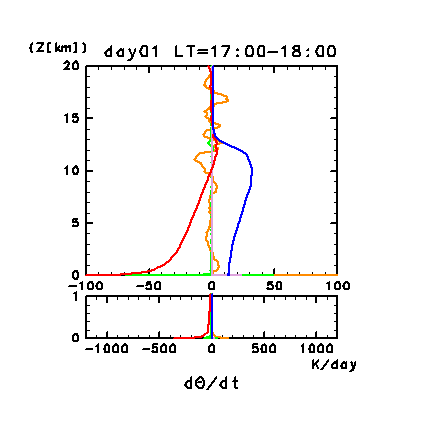
The following four figures show the vertical profiles of the
horizontal and temporal mean heating rates for potential
temperature. Figure 11e
and Figure 11g show such profiles for days 1 and
2 of the dusty case, and Figure 11f
and Figure 11h show profiles for each component
of radiative heating.
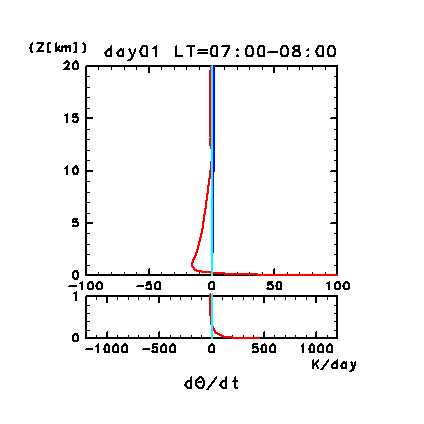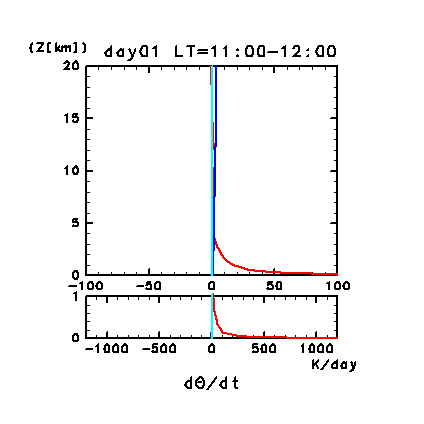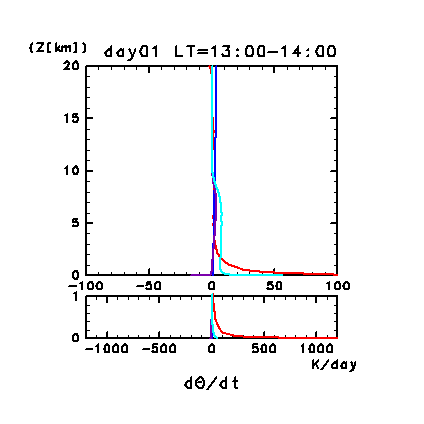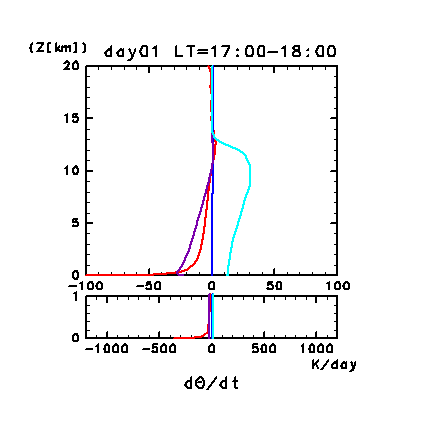
During the daytime after 16:00 LT on day 1, the radiative heating
profile varies greatly in the vertical direction from 10 to 15 km. The
main component of radiative heating, which causes this vertical
variation, is the solar radiative heating associated with dust.
|
|
|
Figure 11e: Horizontal and temporal mean heating rates for
potential temperature on day 1 of the dusty case. Unit is K/day.
Orange line denotes convective heating, red line
denotes infrared radiative heating, blue line denotes solar radiative
heating, green line denotes turbulent diffusion of potential
temperature, and the light purple line denotes heating due to
turbulent dissipation. The lower panel shows a magnified view of the
profiles at altitudes below 1 km.
|
Figure 11f: Diurnal variation of horizontal and temporal mean
radiative heating rates for potential temperature on day 1 of the
dusty case. Unit is K/day. Red line denotes infrared
radiative heating due to CO2, purple line
denotes infrared radiative heating due to dust, blue line denotes near
infrared radiative heating due to CO2, and
the light blue line denotes solar radiative heating due to dust. The
lower panel shows a magnified view of the profiles at altitudes below
1 km.
|
|
|
|
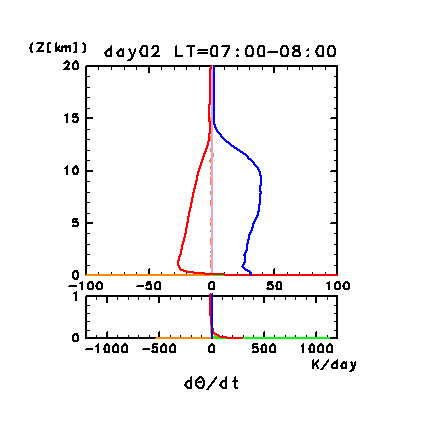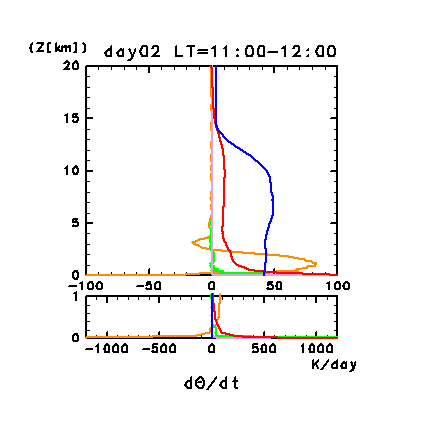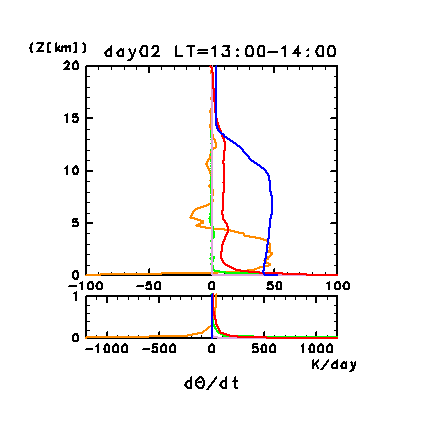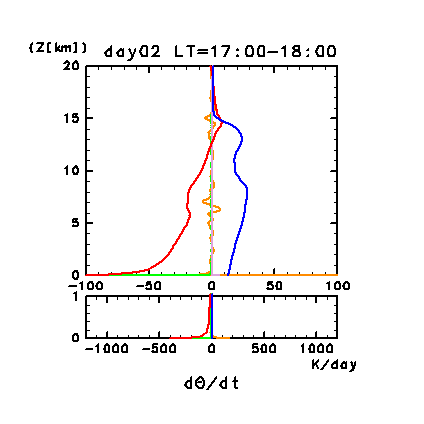
Figure 11g: Horizontal and temporal mean heating rates for
potential temperature on day 2 of the dusty case. Unit is K
/day. Orange line denotes convective heating, red line
denotes infrared radiative heating, blue line denotes solar radiative
heating, green line denotes turbulent diffusion of potential
temperature, and the light purple line denotes heating due to
turbulent dissipation. The lower panel shows a magnified view of the
profiles at altitudes below 1 km.
|
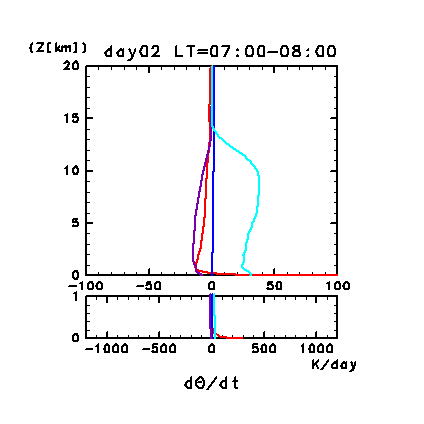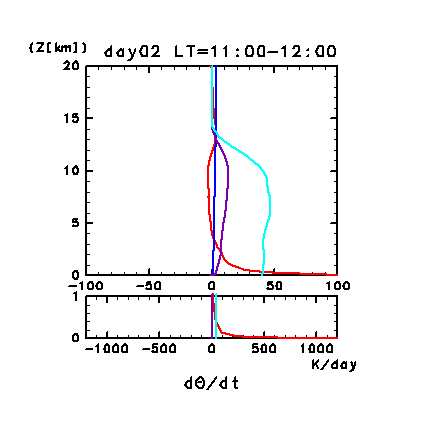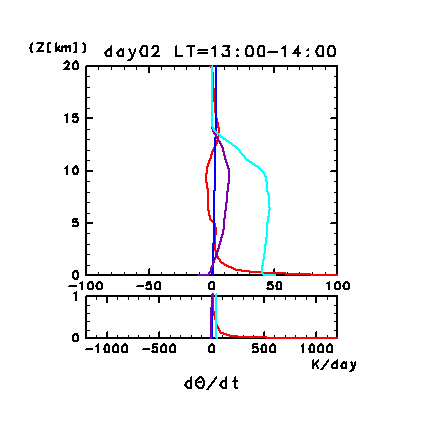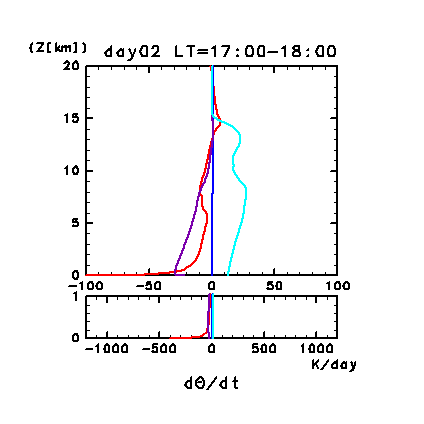
Figure 11h: Diurnal variation of horizontal and temporal mean
radiative heating rates for potential temperature on day 2 of the
dusty case. Unit is K/day. Red line denotes infrared
radiative heating due to CO2, purple line
denotes infrared radiative heating due to dust, blue line denotes near
infrared radiative heating due to CO2, and
the light blue line denotes solar radiative heating due to dust. The
lower panel shows a magnified view of the profiles at altitudes below
1 km.
|
|