|
The monochromatic optical depth 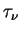 for wave number for wave number 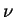 is represented by using the extinction coefficient per unit volume
is represented by using the extinction coefficient per unit volume
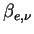 as follows. as follows.
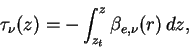 |
(A.39) |
where 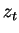 is the altitude at the top of the atmosphere. is the altitude at the top of the atmosphere.
 is given as follows. is given as follows.
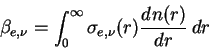 |
(A.40) |
where 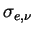 is the extinction cross section and is the extinction cross section and
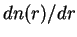 is the size distribution of a scattering particle
(cf. Liou, 1980; Shibata, 1999).
By using the extinction coefficient per unit mass is the size distribution of a scattering particle
(cf. Liou, 1980; Shibata, 1999).
By using the extinction coefficient per unit mass
 ,
Equation (A.40)
is written as follows. ,
Equation (A.40)
is written as follows.
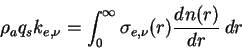 |
(A.41) |
where 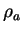 is atmospheric dencity, and is atmospheric dencity, and 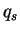 is the mass mixing ratio of a scattering particle.
Similarly, the scattering and absorption coefficient per unit volume
are represented by using the scattering cross section is the mass mixing ratio of a scattering particle.
Similarly, the scattering and absorption coefficient per unit volume
are represented by using the scattering cross section
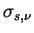 and the absorption cross section and the absorption cross section
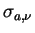 as follows. as follows.
and the single scattering albedo
 is given as follows. is given as follows.
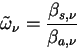 |
(A.44) |
The extinction efficiency 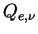 is defined as the ratio of the extinction cross section to the geometric cross section. is defined as the ratio of the extinction cross section to the geometric cross section.
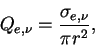 |
(A.45) |
Similarly, the scattering efficiency 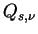 and absorption efficiency and absorption efficiency
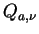 are defined as follows. are defined as follows.
In the present study, dust opacity is derived from the mass mixing
ratio of atmospheric dust 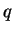 .
The provided parameters include the
cross section weighted mean extinction efficiency .
The provided parameters include the
cross section weighted mean extinction efficiency
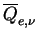 , the single scattering albedo , the single scattering albedo
 , the size distribution function of dust , the size distribution function of dust
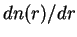 , the effective (i.e., cross section weighted mean) radius , the effective (i.e., cross section weighted mean) radius
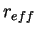 , and the density of a dust particle , and the density of a dust particle
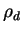 . .
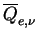 , , 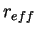 are defined as follows. are defined as follows.
Assuming the shape of a scattering particle is spherical, the
extinction coefficient per unit mass is given as follows.
where 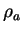 is atmospheric density.
Therefore, optical depth is atmospheric density.
Therefore, optical depth
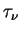 can be represented as follows. can be represented as follows.
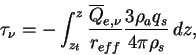 |
(A.51) |
|