|
The dust mass mixing ratio
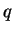 is calculated by using the advection diffusion equation, which
considers the gravitational settling of dust.
is calculated by using the advection diffusion equation, which
considers the gravitational settling of dust.
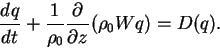 |
(A.19) |
The dust terminal velocity 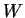 is calculated as follows(Conrath ,1975).
is calculated as follows(Conrath ,1975).
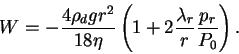 |
(A.20) |
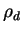 is the density of the dust particle, is the density of the dust particle,
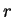 is the radius of the dust particle, is the radius of the dust particle,
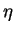 is atmospheric viscosity, is atmospheric viscosity,
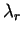 is the mean free path of atmospheric gas at is the mean free path of atmospheric gas at 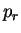 .
In this study, we set .
In this study, we set
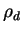 = 3000 kgm-3, = 3000 kgm-3,
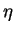 = 1.5×10-5
kgm-1sec-1, = 1.5×10-5
kgm-1sec-1,
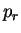 = 25 hPa, = 25 hPa,
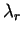 = 2.2×10-6 m.
Equation (A.19)
is applied for each dust particle with a different radius.
However, for simplicity, the radius of a dust particle is assumed to
be equal to the mode radius of a dust particle = 2.2×10-6 m.
Equation (A.19)
is applied for each dust particle with a different radius.
However, for simplicity, the radius of a dust particle is assumed to
be equal to the mode radius of a dust particle
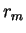 in Equation (A.38),
which is the size distribution function of dust.
in Equation (A.38),
which is the size distribution function of dust.
It is assumed that dust injected from the surface to the atmosphere
occurs when surface stress
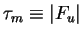 exceeds a threshold value exceeds a threshold value
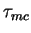 .
The dust flux from the surface .
The dust flux from the surface 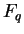 is equivalent to
that obtained by a wind tunnel experiment
(White et al., 1997). is equivalent to
that obtained by a wind tunnel experiment
(White et al., 1997).
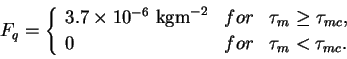 |
(A.21) |
The value of critical surface stress 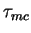 is described in Section 4. is described in Section 4.
|