|
4.b.iv. Heat budget of the atmosphere and surface
|
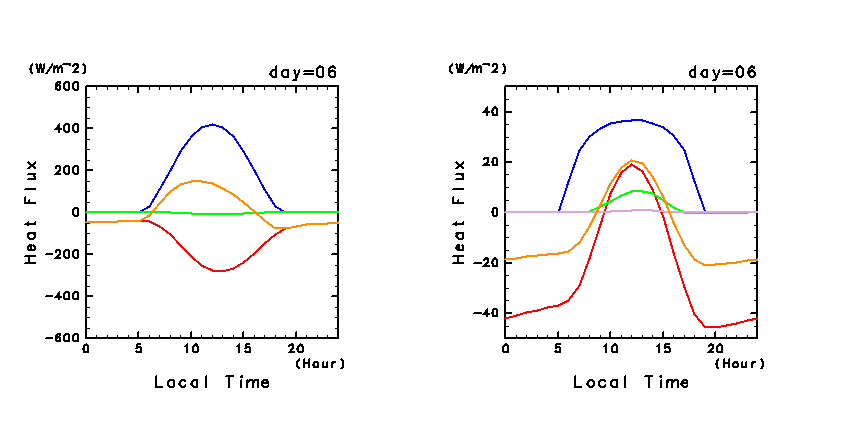
Figure 12f shows the diurnal changes of the
horizontal mean heat budgets at the ground surface and atmosphere for
the dusty case. In each panel, the amount of net heating is almost
equal to that of cooling.
- The amount of net solar radiative heating in the ground layer is
smaller than that of the dust-free case
(Figure 3e). This is caused by
the absorption of solar radiation due to atmospheric dust.
- The amount of net infrared radiative heating due to
CO2 and sensible heating, which are
the dominant contributors in driving convection, are smaller
than those of the dust-free case
(Figure 3e). The sum of these
differences reaches 20 W m-2 during the daytime.
- For the atmosphere, the dominant component of net solar heating
is the absorption of solar radiation due to dust. The amount of
this absorption is similar to the decrease of net solar
radiative flux in the ground layer for the dust-free case.
The reason for the decrease in CO2 infrared
heating is a decrease in ground temperature. This decrease is
approximately on the same order of magnitude of the decrease of the 15
μm-band infrared emission from the ground surface (i.e., several
W m-2). Sensible heating decreases due to a decrease in the
wind velocity associated with convection.
|
Figure 12f: Diurnal changes of the horizontal mean heat budgets
for day 6 of the dusty case. Unit of the vertical axis is W
m-2. (Left panel) Heat budget for the ground layer. Blue
line shows net solar radiative flux (
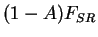 ), red line shows net infrared radiative flux
( ), red line shows net infrared radiative flux
(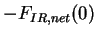 , green line shows sensible heat flux
( , green line shows sensible heat flux
(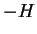 ), and the orange line shows the total
flux. Positive sign indicate heating of the ground
surface. (Right panel) Heat budget for the atmosphere. Blue line
shows net solar radiative heating ( ), and the orange line shows the total
flux. Positive sign indicate heating of the ground
surface. (Right panel) Heat budget for the atmosphere. Blue line
shows net solar radiative heating (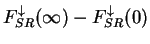 ), red
line shows net infrared radiative heating ( ), red
line shows net infrared radiative heating (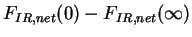 ),
green line shows sensible heating ( ),
green line shows sensible heating (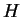 ), purple line
shows heating due to turbulent dissipation, and the orange line shows
the sum of net infrared radiative heating and sensible
heating. Positive sign indicate heating of the atmosphere. ), purple line
shows heating due to turbulent dissipation, and the orange line shows
the sum of net infrared radiative heating and sensible
heating. Positive sign indicate heating of the atmosphere.
|
|