Considering the convection development scenario outlined
in the previous section further,
we can evaluate the convective velocities
induced by the vertical and horizontal temperature differences,
and compare their amplitudes.
The convective velocity induced by the vertical temperature difference
u is obtained from ordinary boundary-layer theory:
|
![u = \left( \Dinv{2 \sqrt{\pi}}\right)^{\frac{2}{3}}\left[ ...{a^{7}}{(1+a^{4})^{2}} \right]^{\Dinv{3}} Ra^{\frac{2}{3}},](img32.gif) |
(10) |
The velocity of convection beneath the plate u'
is estimated by substituting for Ra
in (10)
the value of Ra' in (8).
In light of the comparison above with
the numerical calculations,
we divide equation (10) by
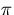 to estimate the velocity amplitudes.
to estimate the velocity amplitudes.
Conversely, the velocity amplitude of the convection induced
by the horizontal temperature difference uh
is determined by the dynamical balance
of the equation of motion at steady state:
|
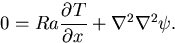 |
(11) |
Differentiating (11)
with respect to z and using
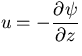 , we obtain
, we obtain
|
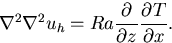 |
(12) |
Temperature difference
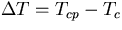 ,
is expressed as a function of the Rayleigh number using
(5) and
(9).
The vertical scale of a convection cell is
Lz=1
and the horizontal scale is
Lx. Then we have
,
is expressed as a function of the Rayleigh number using
(5) and
(9).
The vertical scale of a convection cell is
Lz=1
and the horizontal scale is
Lx. Then we have
|
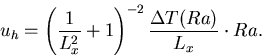 |
(13) |
We divide this equation by
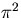 to evaluate the velocity amplitude,
considering that the distributions of the temperature
and stream function are approximately described by
to evaluate the velocity amplitude,
considering that the distributions of the temperature
and stream function are approximately described by
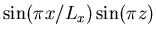 .
.
to estimate the velocity amplitudes.
, we obtain
, is expressed as a function of the Rayleigh number using (5) and (9). The vertical scale of a convection cell is Lz=1 and the horizontal scale is Lx. Then we have
to evaluate the velocity amplitude, considering that the distributions of the temperature and stream function are approximately described by
.