|
4.c.i. Intensity of Convection
|
The depth of conduction layer and potential temperature difference in
the layer can be estimated by using equation
(2) and
(4). Total amount of CO2
infrared radiative heating and sensible heat flux in day time is about
20 W m-2 which is responsible for driving convection
(see Figure 12f). The value of
turbulent diffusion coefficient is almost same as that in dust-free
case (∼ 15 m2 sec-1, see
Figure 12b). Substituting these
values in Equation (2), the value of
vertical gradient of potential temperature in conduction layer is -0.1
K m-1. It is consistent with the results of numerical
simulation (Figure 14). In this case, Equation
(4) which gives 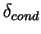 is as
follows. is as
follows.
We obtain
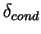 ∼ 60 m,
∼ 60 m,
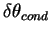 ∼ 6 K (those of numerical simulation results are 50 m and 3 K, respectively).
As compared to estimation in dust-free case,
the value of
∼ 6 K (those of numerical simulation results are 50 m and 3 K, respectively).
As compared to estimation in dust-free case,
the value of
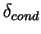 is similar and
is similar and
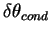 is 2 K smaller.
is 2 K smaller.
The potential temperature deviation of a convective plume is
estimated by using Equation (5).
According to Figure 14, the depth of conduction
layer 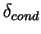 is about 40 m, and temperature difference in
the layer is 3 K. The depth of convection layer is 5000 m.
The value of turbulent diffusion coefficient is almost same as that in
dust-free case (∼ 15 m2 sec-1). Estimated
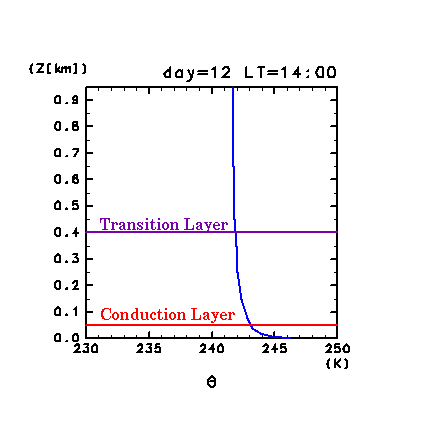
value of potential temperature deviation of a convective plume by
using Equation (5) is as follows. is about 40 m, and temperature difference in
the layer is 3 K. The depth of convection layer is 5000 m.
The value of turbulent diffusion coefficient is almost same as that in
dust-free case (∼ 15 m2 sec-1). Estimated
value of potential temperature deviation of a convective plume by
using Equation (5) is as follows.
|
|
Figure 14:
Vertical profile of horizontal mean potential temperature below the
height of 1 km at 14:00 LT on day 6 for the dusty case.
|
|